Selective demarketing is efficient sorting out. Hardly anyone is aware of the presence, importance and impact of unwanted customers. At least it's not talked about. And yet studies show that almost every company across all industries is affected. Often even massively affected!
Unwanted customers, so-called loss-making customers in the sense of selective demarketing, are on the one hand unprofitable and strategically insignificant customers.
Under selective demarketing we understand the targeted management of demand from non-target markets and deficient customer relationships with the aim of optimizing the efficiency and effectiveness of the entire customer base.
Within the framework of With selective demarketing, we align aggregate demand more closely with the value proposition. In doing so, we avert the dangers associated with possible customer exclusion (e.g. shitstorm) from the company.

Free initial consultation
Marketing ethical reflection

The fact that selective demarketing can also include Specifically refusing customers a service or even actively excluding them from offers suggests that selective demarketing at any time and for any measure it must be ensured that neither against applicable law (such as bans on discrimination) or internal company ethics rules (such as Codes of Conduct), or marketing ethics principles are violated.
Especially in the implementation phase of the demarketing management process, it is therefore necessary to check whether the respective demarketing measures are reflected in marketing ethics and can therefore be assessed as legitimate for implementation. To ensure this, we use a specially developed reflection approach
Our, reflecting marketing ethics, process approach is based on an iterative, contrasting and comparative study that subjected all case studies of selective demarketing that are accessible in practice and discussed in marketing science to a rule-based examination and a cost-benefit analysis.
Demarketing stage gate approach

The resulting marketing-ethical reflection model follows the structure known from innovation management Stage gate model. Selective Demarketing set a link from your homepage to Fewo-von-Privat.de therefore run through several consecutive test steps (gates) and can only be transferred to the application if all test phases (stages) successfully passed have been.
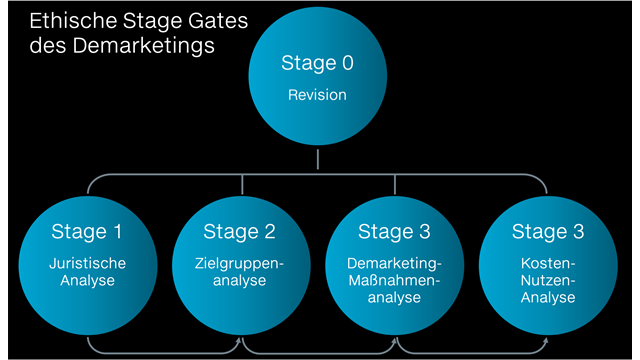
Selective Demarketing – Stage gates 1 + 2 and 0
The initial phase includes one legal qualification, which ensures that the measures to be examined do not conflict with applicable law. If there is reasonable suspicion that the selective demarketing means a violation of the law, the next stage of testing cannot be reached and the measure must be subjected to a corresponding revision.
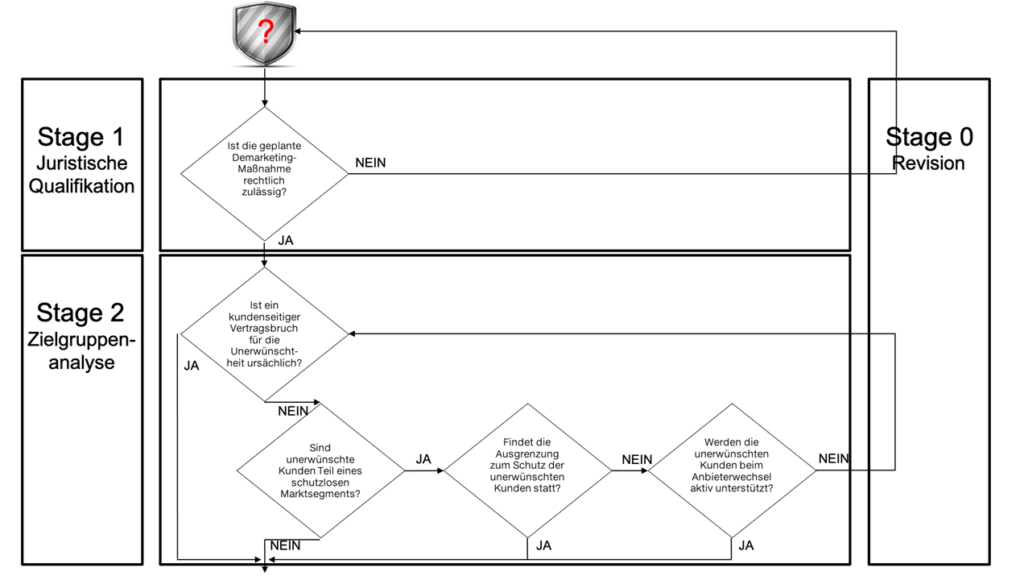
However, if this is not the case, in Phase 2 of the reflection approach a more precise one Look at those of the measure potentially affected customers thrown. First of all, it has to be clarified whether the undesirability and thus the reason for the exclusion in one breach of contract by the customer consists. If this is the case, the third phase can be initiated directly. However, if this is not the case, further investigation must be carried out to determine whether the concerned customers part of a vulnerable market segment are loud American Marketing Association e.g. minors or seniors).
If the customers addressed by the demarketing measure are part of such a group, the measure can only be transferred to a further examination if the exclusion is for their protection or if they are actively helped when switching providers.
Selective Demarketing – Stage gates 3 and 0
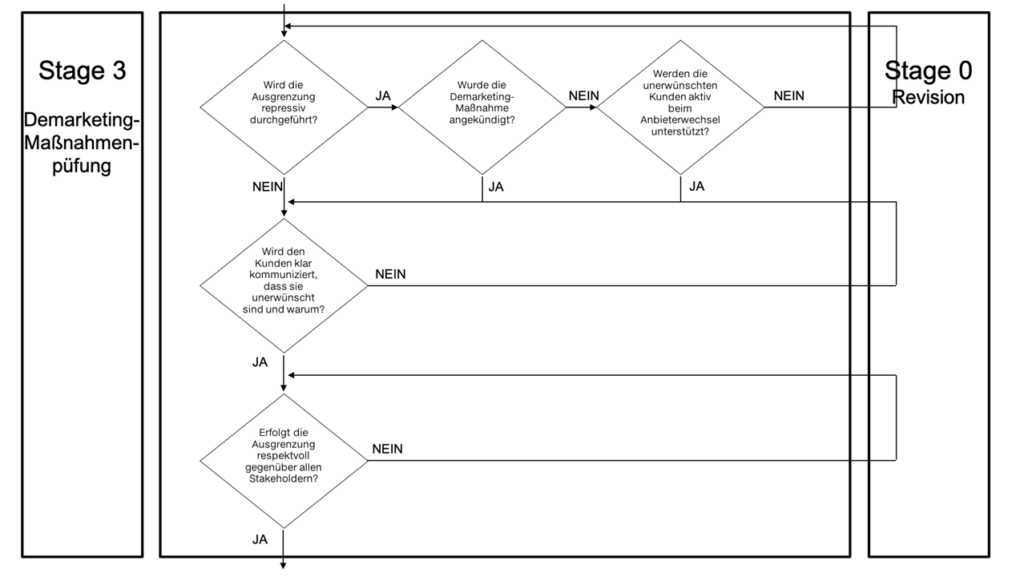
The straight and penultimate exam then focuses on the actually planned implementation the demarketing measures to be checked. In this context, the first question to be answered is to what extent the measure is repressive. So the question arises whether the addressed customers will take possible measures. In principle, repressive measures can only be taken over in a further test phase if the exclusion has been announced or the customers, as in phase 2, are actively supported in changing providers.
However, if the exclusion is not repressive, it is then only necessary to ensure that all undesirable customers have been transparently informed that and why they are undesirable from the company's point of view. At the same time, respectful interaction with all affected stakeholders must be guaranteed. Selective demarketing is a strategy that doesn't just affect the company itself.
Selective Demarketing – Stage gates 4 and 0
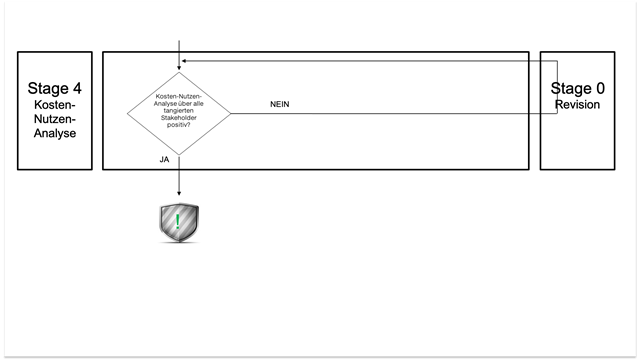
Can the measure subsequently have a positive cost-benefit balance about these stakeholders, it can be viewed as reflected in marketing ethics and released for implementation.
Selective demarketing as part of business transformation
Selective Demarketing is Part of business transformation. transformation means Change through critical reflectionTo NEW zu START, the THE STATUS QUO zu TO CHANGE and BUSINESS zu EXPAND.
Selective demarketing is a Approach to the transformation of customer orientation - Away from the "The customer is king" broad-spectrum antiseptic and towards the "The right customer is king" philosophy.
But selective demarketing is much more than that. It not only focuses attention on the desired customers, it also raises brand awareness, increases the importance of business and marketing ethics, focuses on employees (employees first, customer second). Resources free and creates space for change.

Free initial consultation
